News
What is "super radiant light source"
2024-03-04 11:30:37 | Company News Page views:693
What is "super radiant light source"? How much do you know about it? I hope you can have a good look at the photoelectric micro knowledge brought to you!
Superradiant light source (also known as ASE light source) is a broadband light source (white light source) based on superradiation. (It is often mistakenly called a superluminous source, which is based on a different phenomenon called superfluorescence.) In general, a superradiant light source contains a laser gain medium that radiates light after excitation and then amplifies it to emit light.
Superradiant sources have very low temporal coherence due to their large radiation bandwidth (compared to lasers). This greatly reduces the possibility of light spots, which are often seen in laser beams. However, its spatial coherence is very high, and the output light of the ultra-radiant light source can be well focused (similar to the laser beam), so the light intensity is much higher than that of the incandescent lamp.
It is a very suitable optics coherent light source tomography (OpticalCoherenceTomography, OCT), device characteristics analysis () in optical fiber communication, gyro and optical fiber sensor. See superemitting diodes for more detailed applications.
One of the most main radiation light source for ultra radiation diode (Superluminescent Diodes SLD laser) and optical fiber amplifier. Fibre-based light sources have higher output power, while SLD are smaller and less costly. Both have radiation bandwidths of at least a few nanometers and tens of nanometers, and sometimes even greater than 100 nanometers.
Superradiant light source (also known as ASE light source) is a broadband light source (white light source) based on superradiation. (It is often mistakenly called a superluminous source, which is based on a different phenomenon called superfluorescence.) In general, a superradiant light source contains a laser gain medium that radiates light after excitation and then amplifies it to emit light.
Superradiant sources have very low temporal coherence due to their large radiation bandwidth (compared to lasers). This greatly reduces the possibility of light spots, which are often seen in laser beams. However, its spatial coherence is very high, and the output light of the ultra-radiant light source can be well focused (similar to the laser beam), so the light intensity is much higher than that of the incandescent lamp.
It is a very suitable optics coherent light source tomography (OpticalCoherenceTomography, OCT), device characteristics analysis () in optical fiber communication, gyro and optical fiber sensor. See superemitting diodes for more detailed applications.
One of the most main radiation light source for ultra radiation diode (Superluminescent Diodes SLD laser) and optical fiber amplifier. Fibre-based light sources have higher output power, while SLD are smaller and less costly. Both have radiation bandwidths of at least a few nanometers and tens of nanometers, and sometimes even greater than 100 nanometers.
For all high-gain ASE light sources, optical feedback (e.g., reflection from fiber ports) needs to be carefully suppressed, so it creates a parasitic laser effect. For optical fiber devices, Rayleigh scattering inside the optical fiber will affect the final performance index.
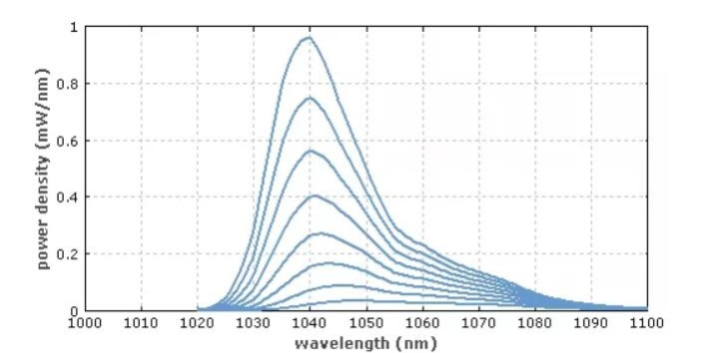
Figure 1: The ASE spectrum produced by the fiber amplifier is calculated as a curve at different pump powers. As the power increases, the spectrum moves towards the shorter wavelength (the gain increases rapidly) and the spectral line Narrows. Wavelength shifting is normal for quasi-three-level gain media, while line narrowing occurs in almost all superradiant sources.